Developer Guide

BudgetBaby 

BudgetBaby is a budget and expenses tracking desktop app for University students and/or those who are looking to better manage their finances. It is optimized for use via a Command Line Interface (CLI) so that entering and editing financial records and budgets can be done faster by typing in commands while still having the benefits of a Graphical User Interface (GUI).
Table of Contents
- 1 About
- 2 Setting Up, Getting Started
- 3 Design
- 4 Implementation
- 5 Appendix: Requirements
- 6 Appendix: Instructions for Manual Testing
1 About
This document serves as a guide for developers to understand the overall architecture and design of the BudgetBaby application. It should help new developers and existing developers understand how different parts of the codebase work together to achieve different functionalities.
2 Setting up, getting started
Refer to the guide Setting up and getting started.
3 Design
3.1 Architecture
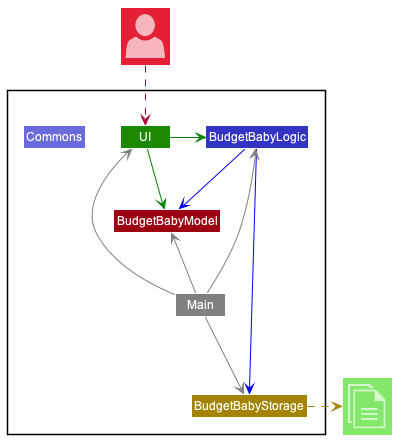
The Architecture Diagram given above explains the high-level design of the App. Given below is a quick overview of each component.
.puml files used to create diagrams in this document can be found in the diagrams folder. Refer to the PlantUML Tutorial at se-edu/guides to learn how to create and edit diagrams.
Main has two classes called Main and MainApp. It is responsible for,
- At app launch: Initializes the components in the correct sequence, and connects them up with each other.
- At shut down: Shuts down the components and invokes cleanup methods where necessary.
Commons represents a collection of classes used by multiple other components.
The rest of the App consists of four components.
-
UI: The UI of the App. -
BudgetBabyLogic: The command executor. -
BudgetBabyModel: Holds the data of the App in memory. -
BudgetBabyStorage: Reads data from, and writes data to, the hard disk.
Each of the four components,
- defines its API in an
interfacewith the same name as the Component. - exposes its functionality using a concrete
{Component Name}Managerclass (which implements the corresponding APIinterfacementioned in the previous point.
For example, the BudgetBabyLogic component (see the class diagram given below) defines its API in the BudgetBabyLogic.java interface and exposes its functionality using the BudgetBabyLogicManager.java class which implements the BudgetBabyLogic interface.
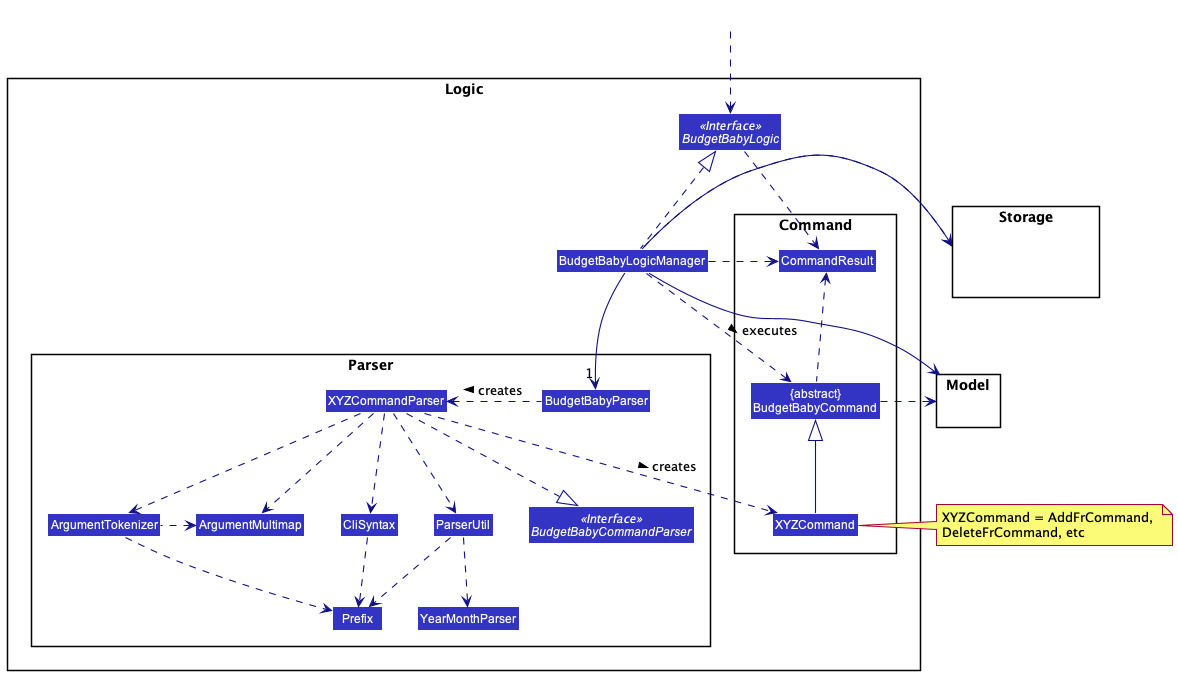
How the architecture components interact with each other
The Sequence Diagram below shows how the components interact with each other for the scenario where the user issues the command add-fr d/Lunch a/10.
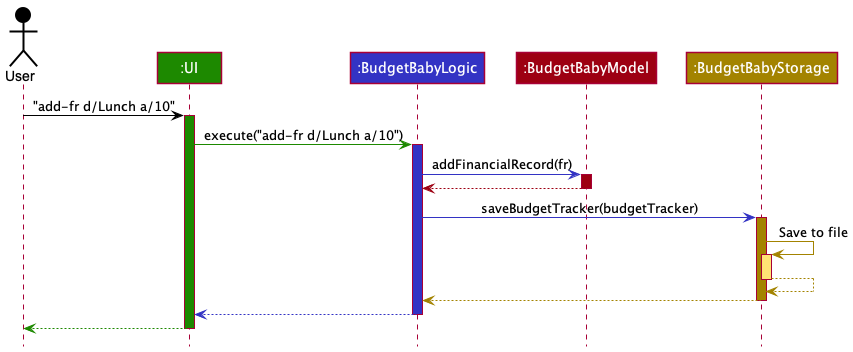
The sections below give more details of each component.
3.2 UI component
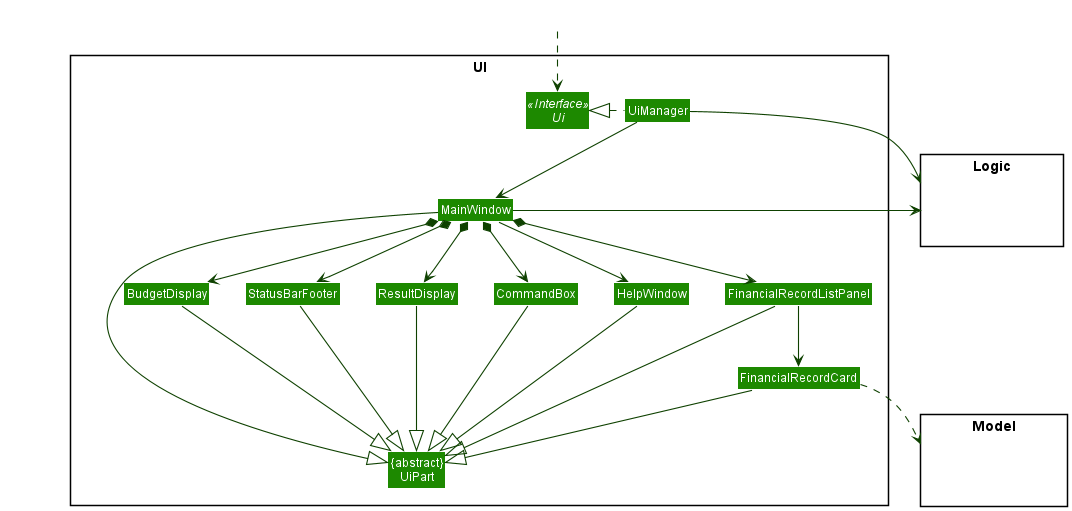
API :
Ui.java
The UI consists of a MainWindow that is made up of parts. It is made up of a HelpWindow, BudgetDisplay, FinancialRecordListPanel, CommandBox, ResultDisplay and a StatusBarFooter. All these, including the MainWindow, inherit from the abstract UiPart class.
The UI component uses JavaFx UI framework. The layout of these UI parts are defined in matching .fxml files that are in the src/main/resources/view folder. For example, the layout of the MainWindow is specified in MainWindow.fxml
The UI component,
- Executes user commands using the
Logiccomponent. - Listens for changes to
Modeldata so that the UI can be updated with the modified data.
3.3 Logic component

API:
BudgetBabyLogic.java
-
BudgetBabyLogicuses theBudgetBabyParserclass to parse the user command. - This results in a
BudgetBabyCommandobject which is executed by theBudgetBabyLogicManager - The command execution can affect the
BudgetBabyModel(e.g. adding a financial record). - The result of the command execution is encapsulated as a
CommandResultobject which is passed back to theUi. - In addition, the
CommandResultobject can also instruct theUito perform certain actions, such as displaying help to the user.
Given below is the sequence diagram for interactions within the Logic component for the execute("add-fr d/Lunch a/10") API call.
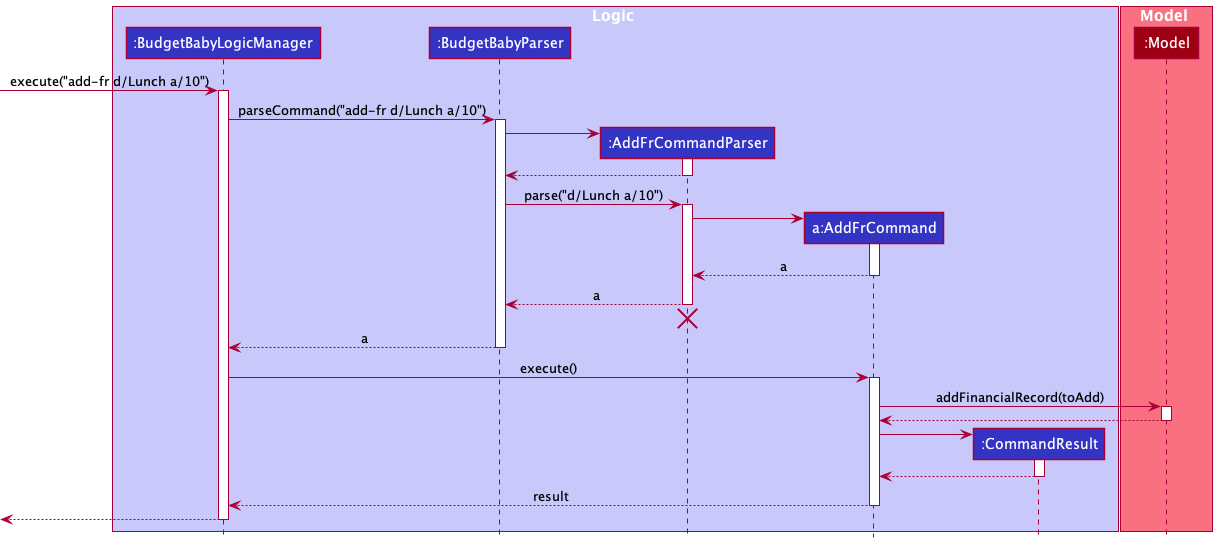
AddFrCommandParser should end at the destroy marker (X) but due to a limitation of PlantUML, the lifeline reaches the end of diagram.
3.4 Model component
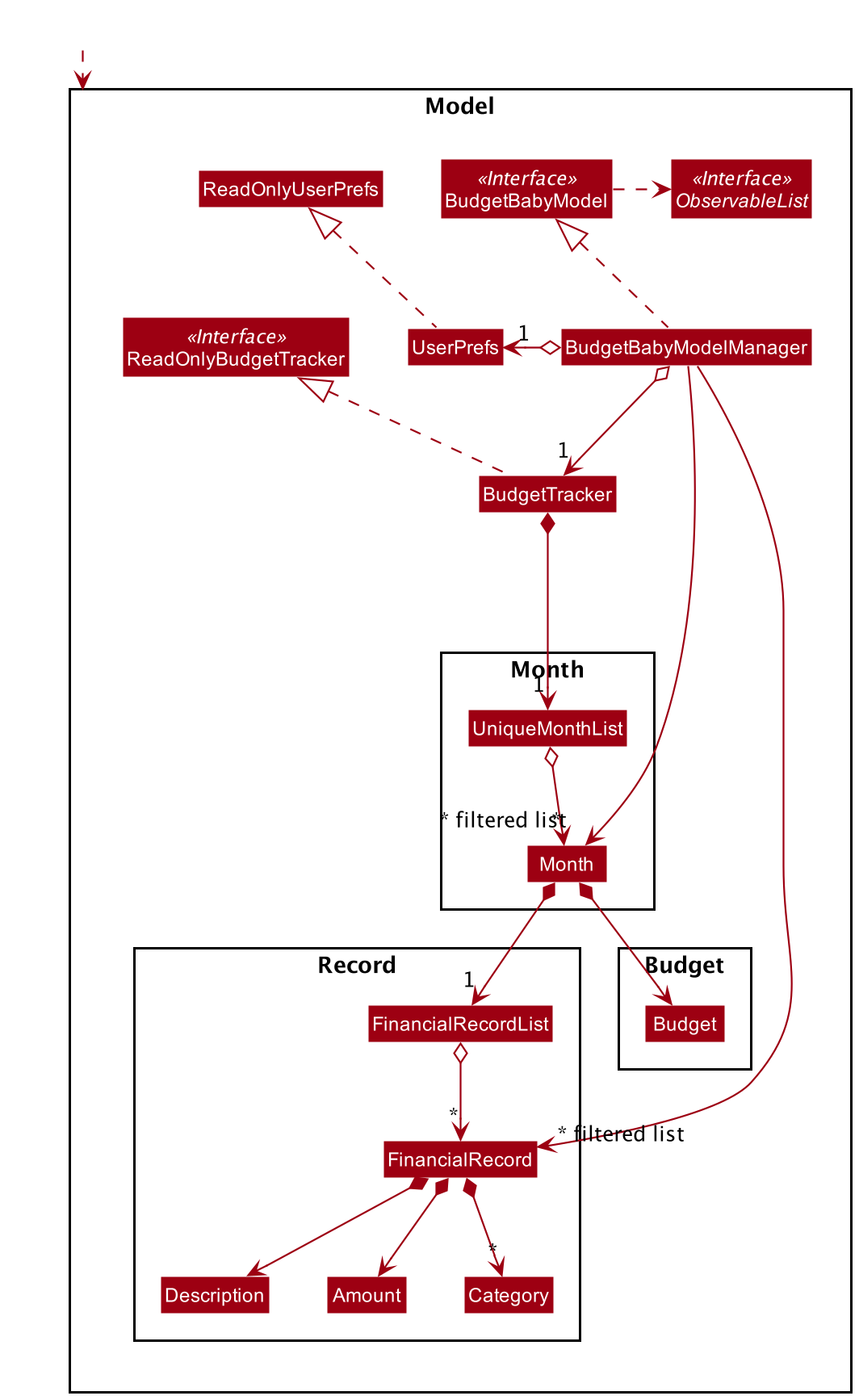
API : BudgetBabyModel.java
The BudgetBabyModel,
- stores a
UserPrefobject that represents the user’s preferences. - stores the budget tracker data.
- exposes an unmodifiable
ObservableList<Month>that can be ‘observed’ e.g. the UI can be bound to this list so that the UI automatically updates when the data in the list change. - exposes an unmodifiable
ObservableList<FinancialRecord>that can be ‘observed’ (same as above) - does not depend on any of the other three components.
3.5 Storage component
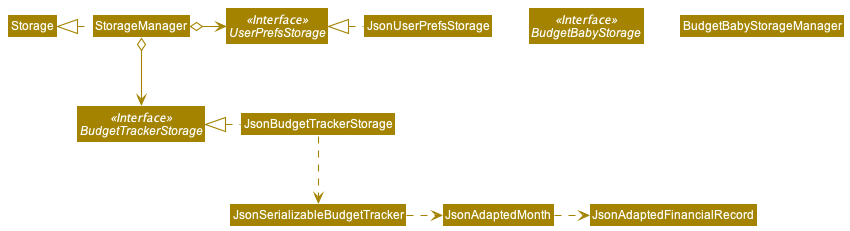
API : BudgetBabyStorage.java
The Storage component,
- can save
UserPrefobjects in json format and read it back. - can save the budget tracker data in json format and read it back.
3.6 Common classes
Classes used by multiple components are in the seedu.budgetbaby.commons package.
4 Implementation
This section describes some noteworthy details on how certain features are implemented.
4.1 Month Management Feature
Month is a very important concept in our application. As a budget tracker, we keep track of users’
financial records every month and a monthly budget can be set, which represents their spending goal
of the month. As such, a Month can be seen a building block of the budget tracker, and our application,
the budget tracker consists of many unique months, of which each represents an actual month in real life.
Actual Implementation
In order to introduce this Month concept to our application, we used two models, Month and UniqueMonthList. UniqueMonthList consists of a list of Month where every two months in the list
must be unique, just like in real life, no two months will be the same. Our BudgetTracker model will then contain this UniqueMonthList representing the months which have records in our application. Please refer to
Model Component for class diagram illustrating this relationship.
In our BudgetTracker class, we also keep a single Month reference to the currentDisplayMonth. currentDisplayMonth represents the month that is currently being dispayed on the application. As can be seen from the Ui of our application, at one time, only the associated data of one particular month is being displayed. Every time currentDisplayMonth is updated, we will notify the observers of this object, and thus the Ui will be updated correspondingly.
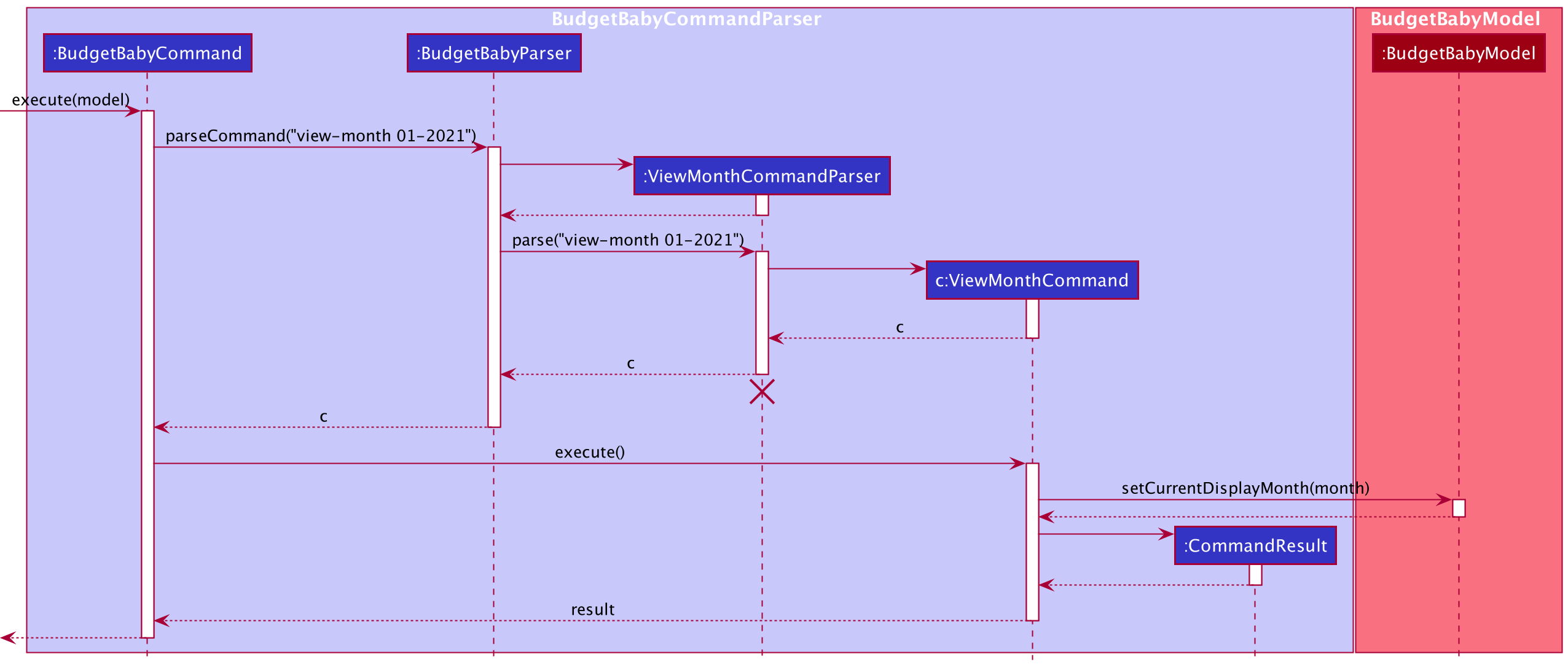
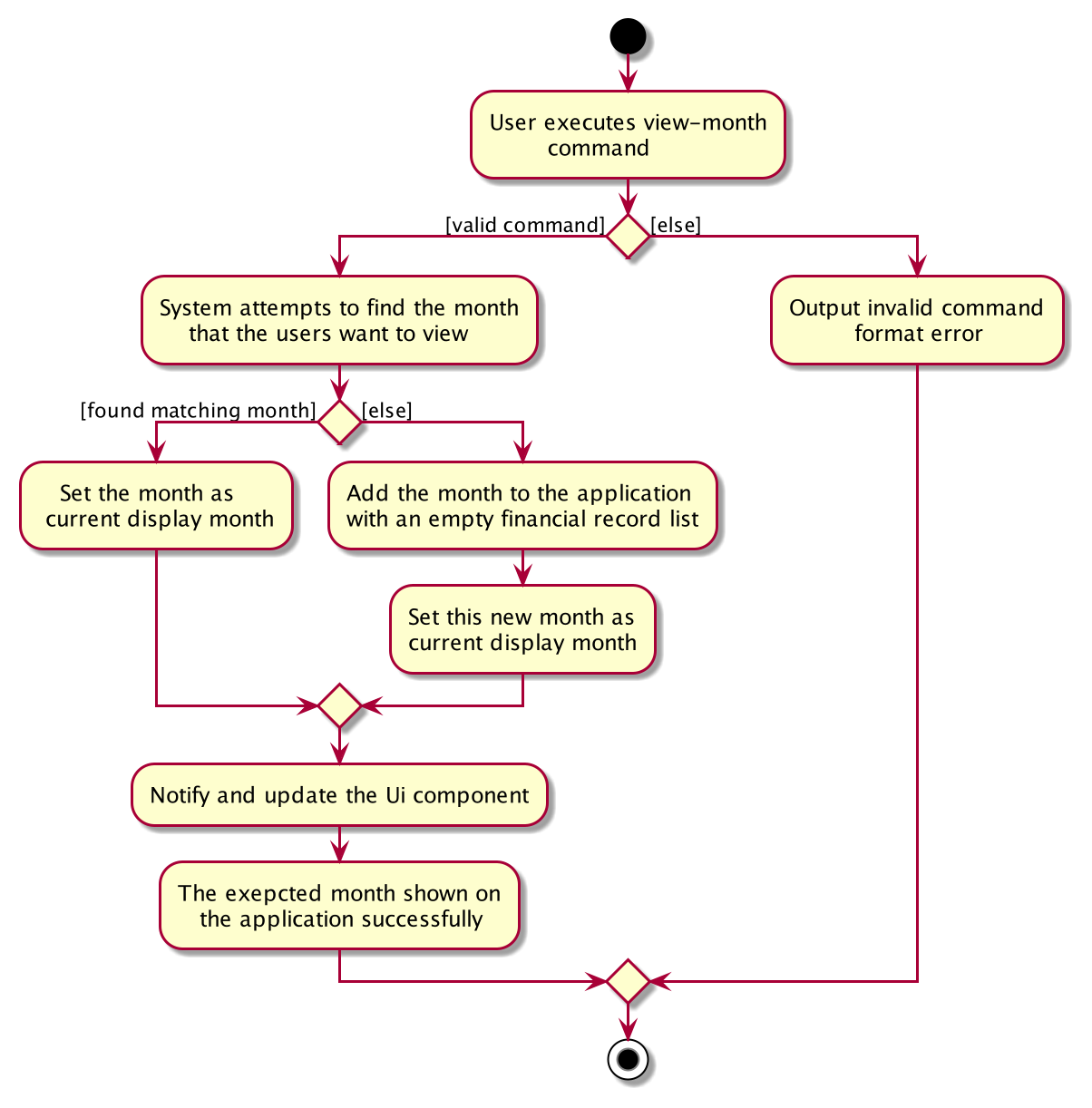
view-month command
view-month is the command that users use to change the Ui to display information on another month. Similar to the mechanism described in Logic Component, view-monthcommand goes through its own ViewMonthCommandParserto produce a ViewMonthCommand, and when the command is executed, the currentDisplayMonth of the budget tracker is updated and this change is reflected on the Ui through an Observer Pattern.
The following sequence diagram shows how the view-month operation works:
The following activity diagram summarizes what happens when a user executes find-fr:
4.2 Financial Record Management Feature
FinancialRecord is another important concept in our application. A financial record represents one record of expense that users key in to store in the budget tracker. Each FinancialRecord consists of a Description, Amount, Timestamp and potentially Categories. Each Month then contains a FinancialRecordList which is essentially a list of FinancialRecord
add-fr command
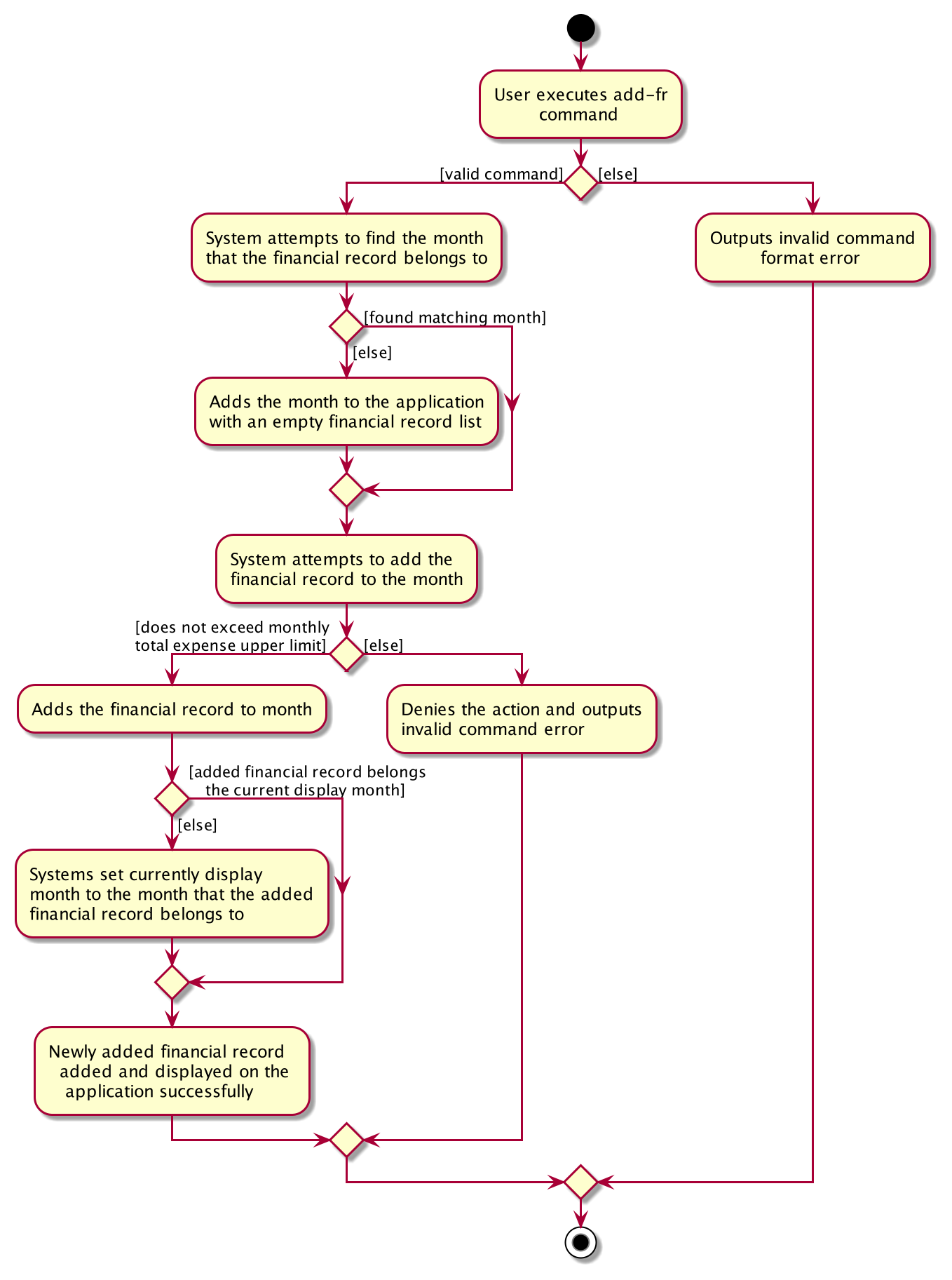
The proposed add-fr mechanism is facilitated by BudgetBabyModelManager which contains
a BudgetTracker object in which FinancialRecord can be added.
The command is parsed from BudgetBabyCommandParser to the AddFrCommandParser class,
where the input fields will be processed before instantiating a new valid AddFrCommand.
The AddFrCommand calls the addFinancialRecord method of the BudgetBabyModel that
is implemented by BudgetBabyModelManager. BudgetBabyModelManager then handles the
adding of the new FinancialRecord to the BudgetTracker. Inside the BudgetTracker, the corresponding Month that the FinancialRecord belongs to will be found first based on the FinancialRecord’s Timestamp, then the FinancialRecord will be added to the FinancialRecordList of the Month, if the Amount of the FinancialRecordList will not cause the total expense of the month to exceed the upper limit of $1,000,000. If there is any invalid input in this process or if the FinancialRecord cause the totally monthly expense to exceed the upper limit, an exception will be thrown and the command will be denied.
The add-fr commands expects minimally a Description and a Amount for the FinancialRecord. The default Timestamp will be the date when the FinancialRecord is added to the application. The user can also specify a Timestamp which is also referred as Date, as only the date of the timestamp is stored in our application. The user can also tag the FinancialRecord with Categorys.
Extensions Implemented
One extension that we implemented regarding the add-fr feature is that after a FinancialRecord is successfully added, we check if the FinancialRecord belongs to the Month that is currently being displayed. If not, we will switch the currentDisplayMonth to the month that the new FinancialRecord belongs to. We implement this extension in order to improve the overall user experience, as users are likely to want to see the newly added FinancialRecord on the screen to be assured that their action has been successful.
The following activity diagram summarizes what happens when a user executes add-fr:
edit-fr command
Similar to add-fr command, edit-fr command goes through relevant logic components and model managers in the similar manner to edit an existing FinancialRecord in the application.
The edit-fr command expects a minimum of 1 and up to 4 of the following types of arguments: Description, Amount, Timestamp and Category (accept more than more Category). The user needs to provide a Index in the currently dispalying list of FinancialRecord to specify the FinancialRecord that he/she wants to edit. Once we confirm the Index is valid, the relevant data of FinancialRecord will then be replaced with the new data that the user provided. For the four types of arguments that users provide, we replace the existing data completely with the new data provided. To be more specific, if a user include Category argument in his/her edit-fr command, all existing Category of the FinancialRecord will be removed and replaced with the new Category(s) provided by the user.
The edit-fr command has primarily the same set of checks as add-fr, and it also check if the new Amount for the FinancialRecord (if there is one) will cause the total expense of the month to exceed.
delete-fr command
The delete-fr command simply remove the financial record from the Month that it belongs to, and hence from the BudgetTracker. Only one argument which is the Index of the FinancialRecord in the currently displaying list of FinancialRecord needs to be provided to execute this command.
Extensions Implemented
One extension implemented to the delete-fr command is the support for multiple deletion at once. It was difficult to support multiple deletion because whenever a FinancialRecord in the associated list within the current month is removed, it may possibly update the index of all future FinancialRecord within the list after it. The simplest solution used was to sort the indices List<Index> in descending order, by removing the FinancialRecord with the greatest Index first it circumvents the issue since the removal of a FinancialRecord with a greater Index will not affect the Index of all the FinancialRecord before it.
4.3 Budget Management Feature
This section describes how the budget was implemented in our application. To model the user’s budget, Budget is used which represents such an abstraction and wraps an amount stored as a double. Each Month is associated with a respective Budget. By default, the amount stored within a Budget is set to 1000, though this can be changed easily by modifying the DEFAULT_BUDGET field.
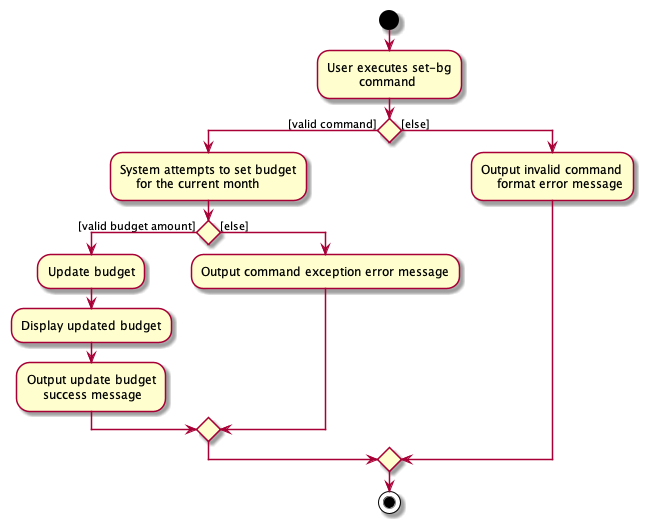
set-bg command
The set-bg command results in the specified BG_AMOUNT being set for the current month as well as the future year ahead. Note that the BG_AMOUNT is compulsory and must be a positive number up to two decimal places. A realistic upper limit has been set on BG_AMOUNT of 1000000 to prevent issues with the UI displaying numbers that are too large.
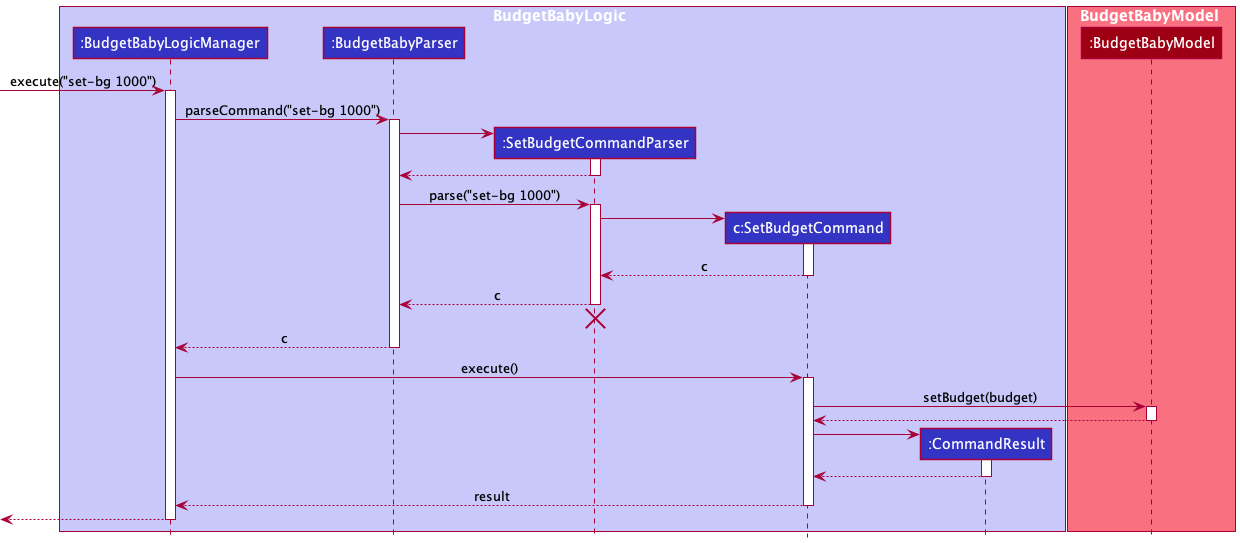
When the command is executed, a concrete SetBudgetCommand is created containing a concrete Budget which has the respective amount that corresponds to what the user keyed in.
The SetBudgetCommand implements SetBudgetCommand#execute method. A concrete BudgetBabyLogicManager handles the execution of the SetBudgetCommand and makes appropriate calls to update the BudgetBabyModel.
Below is a sequence diagram and explanation of how the SetBudgetCommand is executed for the `execute(“set-bg 1000”) API call.
The following activity diagram summarizes what happens when a user executes set-bg:
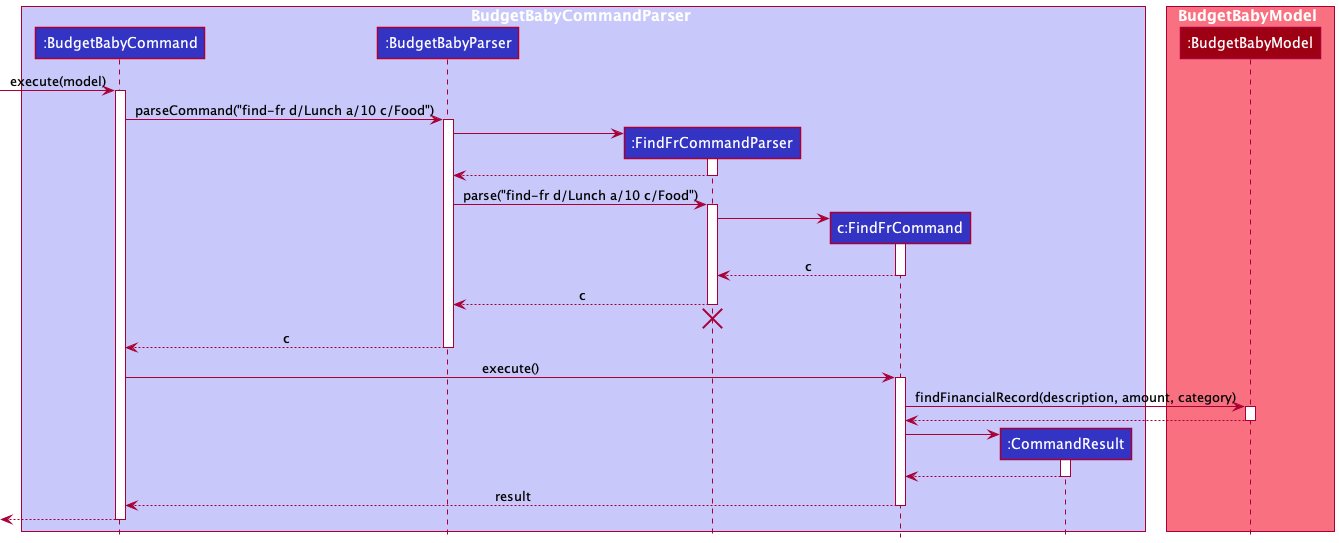
4.4 Find Financial Record Feature
find-fr command
The proposed find mechanism is facilitated by BudgetBabyModelManager which contains
a filtered list filteredFinancialRecords that is to be altered and displayed to the
user according to the find-fr command.
The command is parsed from BudgetBabyCommandParser to the FindFrCommandParser class,
where the input fields will be processed before instantiating a new valid FindFrCommand.
The FindFrCommand calls the findFinancialRecord method of the BudgetBabyModel that
is implemented by BudgetBabyModelManager. BudgetBabyModelManager then handles the
filtering of filteredFinancialRecords through the updateFilteredFinancialRecordList
method. The updated financial records are then displayed to the user on the front end of
the application.
The findFinancialRecord method expects a minimum of 1 and up to 3 of the following arguments:
Description, Amount, Category.
Given below is an example usage scenario and how the find mechanism behaves at each step.
Step 1. The user launches the application for the first time. The filteredFinancialRecords list
presented to the user would be a list of all financial records retrieved from local storage
budgetbaby.json (if applicable).
Step 2. The user executes find-fr d/Lunch a/10 c/Food command to find financial records with
description Lunch, amount 10 and category Food. The find-fr command indirectly calls the
updateFilteredFinancialRecordList method, causing filteredFinancialRecords to display the matching
records without modifying the contents of the original financial records list.
- Note: If no matching financial record(s) is/are found, then the list will not be updated and a log message indicating no records found will be shown.
The following sequence diagram shows how the find operation works:
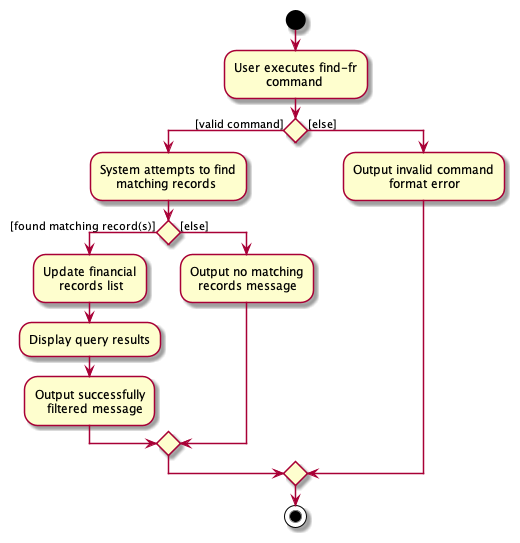
The following activity diagram summarizes what happens when a user executes find-fr:
Extensions Implemented
-
c/FR_CATEGORYfield accepts multiple categories - User is able to delete
Categorythrough theedit-frcommand - Display an appropriate message if no matching financial records found
Design Consideration
-
Alternative 1 (selected choice): A single
find-frcommand that handles all fields- Pros: Eliminates the need to implement separate search features. Allows filtering multiple fields in a single command
- Cons: May cause confusion in usage. Some users may find it cumbersome to deal with
d/a/c/tags
-
Alternative 2: Separate
find-description,find-amount,find-categorycommands- Pros: May be less confusing to users and eliminates the use of
d/a/c/tags - Cons: Additional implementation and commands. More steps required for user when filtering multiple fields
- Pros: May be less confusing to users and eliminates the use of
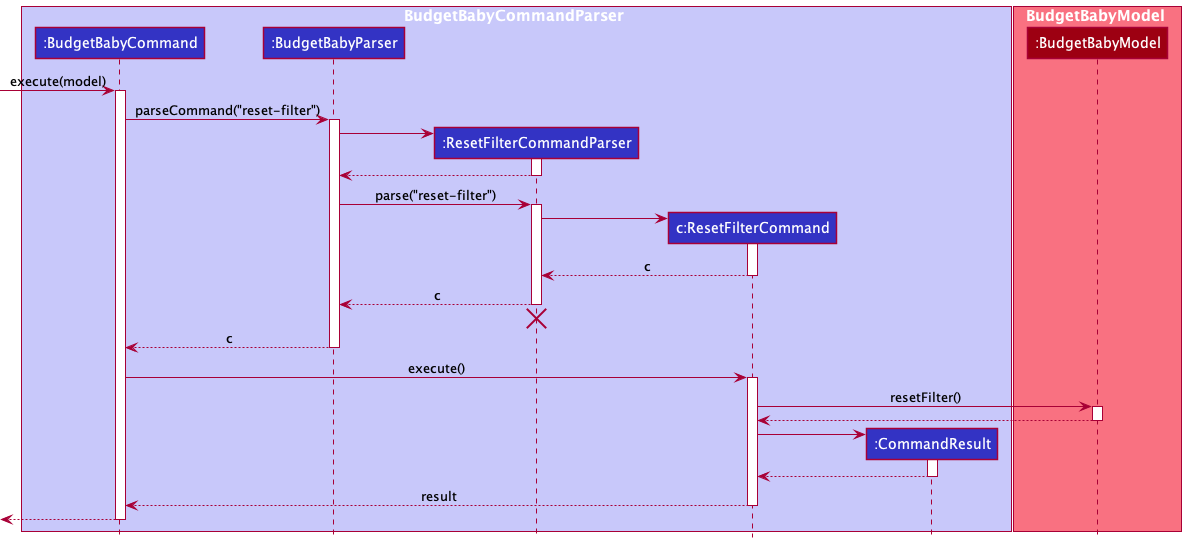
4.5 Reset Filter Feature
reset-filter command
This feature was developed in conjunction with find-fr. As the financial records list can
be filtered to the flags set by the user, there must be a way for the user to revert this list
back to its original state (i.e. displaying all financial records).
Similar to the mechanism of the find operation, the ResetFilterCommand calls
The ResetFilterCommand calls the resetFilter method of the BudgetBabyModel that
is implemented by BudgetBabyModelManager. BudgetBabyModelManager then handles the
resetting of filter on filteredFinancialRecords through the updateFilteredFinancialRecordList
method. The updated original financial records are then displayed to the user on the
front end of the application.
Given below is an example usage scenario and how the reset mechanism behaves at each step
with the find-fr command initially applied
Step 1. The user executes find-fr d/Lunch a/10 c/Food command which filters and displays
the updated financial records list
Step 2. The user is satisfied with his query result and wishes to revert the financial records
list back to its original state. The reset-filter command is executed which indirectly calls the
updateFilteredFinancialRecordList method, causing filteredFinancialRecords to display all
available financial records.
The following sequence diagram shows how the find operation works:
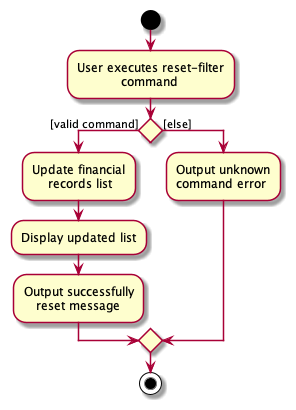
The following activity diagram summarizes what happens when a user executes reset-filter:
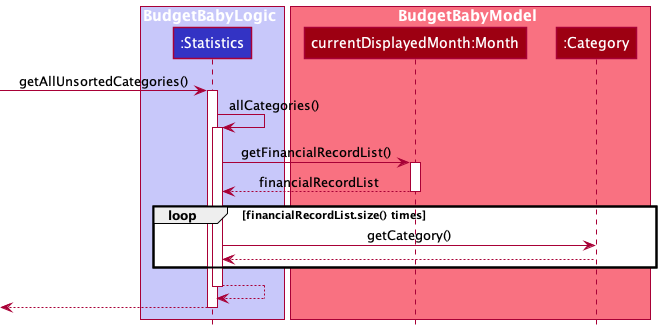
4.6 All Categories Statistics Feature
Implementation
The getAllUnsortedCategories() function in Statistics relies on another method, allCategories() within the same Statistics class.
The allCategories() method obtains the currentDisplayedMonth Month object via the local variable monthList and uses the
getFinancialRecordList() method from the currentDisplayedMonth object.
After obtaining the financialRecordList from the Month object,
the FinancialRecords in the list are looped through, and Category objects are added to a HashMap, along with their respective Amounts.
The HashMap is converted into an ArrayList and is returned.
The following sequence diagram shows how the categories statistics feature works:
4.7 Top 5 Categories Statistics Feature
Implementation
The getTopCategories() feature is based off the previous getAllUnsortedCategories() feature, except that the final returned
ArrayList objects is sorted by the Category amounts and limited to 5 categories using the stream limit method.
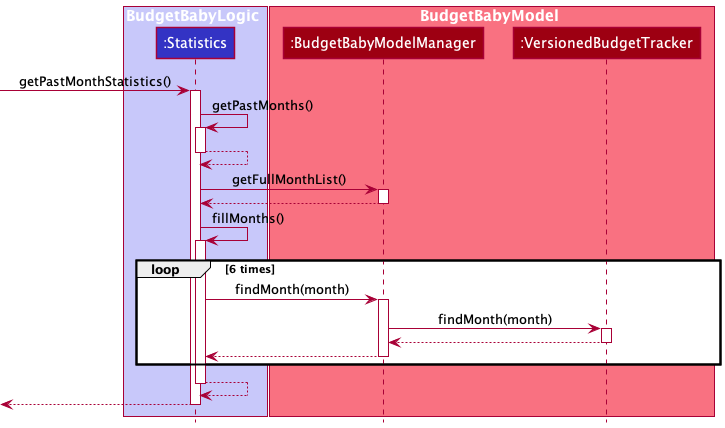
4.8 Past 6 Months Statistics Feature
Implementation
This feature was developed with the help of BudgetBabyModel and BudgetBabyModelManager,
which allowed for the method calls required for this feature to function as required.
The method getPastMonthStatistics() from the Statistics class is called to trigger this feature.
It calls getPastMonths() within Statistics. Within getPastMonths(), the method of getFullMonthsList from BudgetBabyModel which was implemented by
BudgetBabyModelManager was used to obtain the UniqueMonthList object from VersionedBudgetTracker as an ObservableList.
The getPastMonths() method in Statistics calls upon a private method fillMonths() which obtains the monthList
object within the Statistics class which refers to the currentDisplayMonth in VersionedBudgetTracker.
fillMonths() runs through a loop which calls upon the findMonth function from BabyBudgetModelManager, searching for
the most recent 6 months with regard to the currentDisplayMonth, inclusive. If the month does not yet exist due to no
add-fr commands adding Financial Records or no view-month called onto that month, then the month will be created and
added to the UniqueMonthList object in VersionedBudgetTracker.
The following sequence diagram showcases the sequence of events whenever the getPastMonthStatistics() method is called:
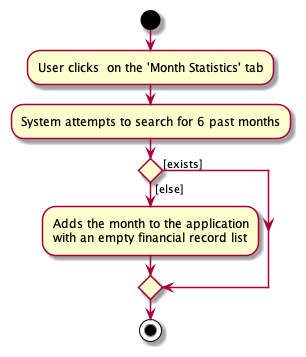
The following activity diagram summarizes the flow of events when the Ui calls upon the getPastMonthStatistics() method:
4.9 Undo Feature
The undo and redo features was developed with the help of VersionedBudgetTracker.
VersionedBudgetTracker is an extension of BudgetTracker which internally stores and handle a list of BudgetTracker states.
A currentStatePointer is used internally to access the different states of the BudgetTracker list.
The additional methods that were implemented are:
-
VersionedBudgetTracker#commit()– Saves the current budget tracker state. -
VersionedBudgetTracker#undo()– Restores to the previous budget tracker state. -
VersionedBudgetTracker#redo()– Restores to the next budget tracker state.
These additional methods are exposed in the BudgetBabyModel interface as BudgetBabyModel#commitBudgetTracker(),
BudgetBabyModel#undoBudgetTracker() and BudgetBabyModel#redoBudgetTracker() respectively.
Given below is an example usage scenario and how the undo/redo mechanism behaves at each step.
Step 1. The user launches the application for the first time. The VersionedBudgetTracker will be initialized with the
initial budget tracker state, and the currentStatePointer pointing to that single budget tracker state.

Step 2. The user executes add-fr d/Ramen a/5.0 command to add a financial record with “Ramen” as description and at
the price of $5.00 in the budget tracker. The add-fr command calls BudgetBabyModel#commitBudgetTracker(), causing
the modified state of the budget tracker after the add-fr d/Ramen a/5.0 command executes to be saved in the
budgetTrackerStateList, and the currentStatePointer is shifted to the newly inserted budget tracker state.
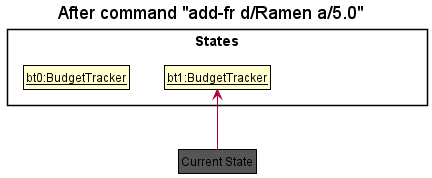
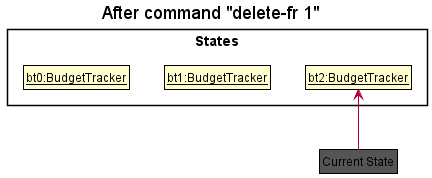
Step 3. The user executes delete-fr 1 to delete the first record in the financial record list. The delete command
also calls BudgetBabyModel#commitBudgetTracker(), causing another modified budget tracker state to be saved into the
budgetTrackerStateList.
[NOTE]
If a command fails its execution, it will not call BudgetBabyModel#commitBudgetTracker(), so the budget tracker state
will not be saved into the budgetTrackerStateList.
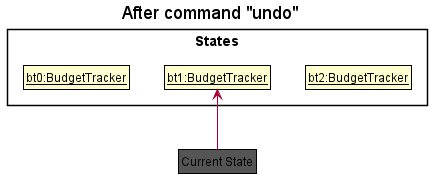
Step 4. The user now decides that adding the person was a mistake, and decides to undo that action by executing the
undo command. The undo command will call BudgetBabyModel#undoBudgetTracker(), which will shift the
currentStatePointer once to the left, pointing it to the previous budget tracker state, and restores the
budget tracker to that state.
[NOTE]
If the currentStatePointer is at index 0, pointing to the initial budget tracker state, then there are no previous
budget tracker states to restore. The undo command uses BudgetBabyModel#canUndoBudgetTracker() to check if this is
the case. If so, it will return an error to the user rather than attempting to perform the undo.
The following sequence diagram shows how the undo operation works:
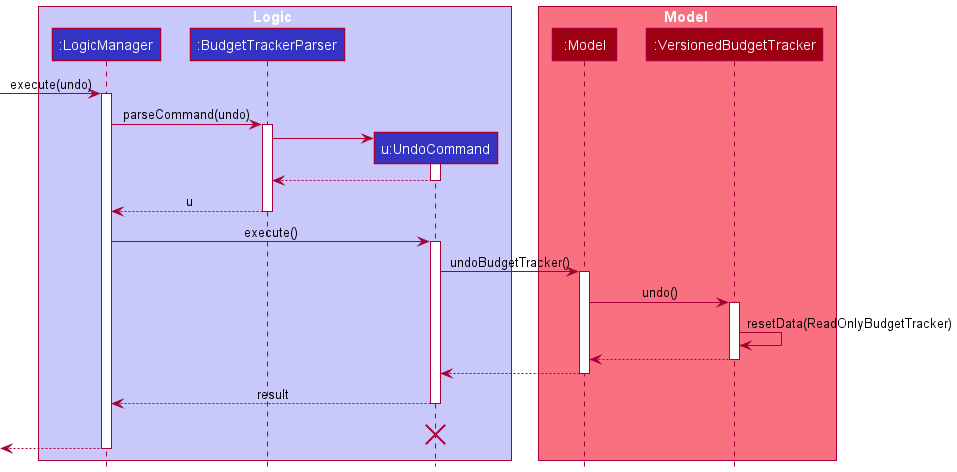
NOTE: The lifeline for UndoCommand should end at the destroy marker (X) but due to a limitation of PlantUML, the
lifeline reaches the end of diagram.
The redo command does the opposite – it calls BudgetBabyModel#redoBudgetTracker(), which shifts the
currentStatePointer once to the right, pointing to the previously undone state, and restores the
budget tracker to that state.
[NOTE]
If the currentStatePointer is at index budgetTrackerStateList.size() - 1, pointing to the latest budget tracker
state, then there are no undone budget tracker states to restore. The redo command uses
BudgetBabyModel#canRedoBudgetTracker() to check if this is the case. If so, it will return an error to the user
rather than attempting to perform the redo.
Step 5. The user then decides to execute the command filter-reset. Commands that are not being supported by undo/redo,
such as filter-reset, will usually not call BudgetBabyModel#commitBudgetTracker(),
BudgetBabyModel#undoBudgetTracker() or BudgetBabyModel#redoBudgetTracker(). Thus, the budgetTrackerStateList
remains unchanged.
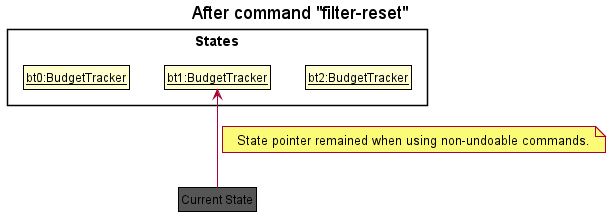
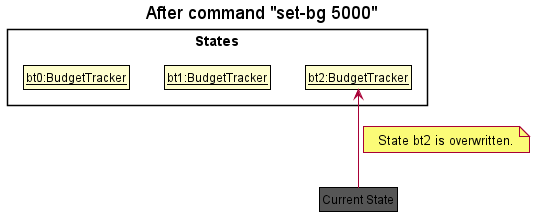
Step 6. The user executes set-bg 5000, which calls BudgetBabyModel#commitBudgetTracker(). Since the
currentStatePointer is not pointing at the end of the budgetTrackerStateList, all budget tracker states after the
currentStatePointer will be purged. We designed it this way because it no longer makes sense to redo the
set-bg 5000 command. This is the behavior that most modern desktop applications follow.
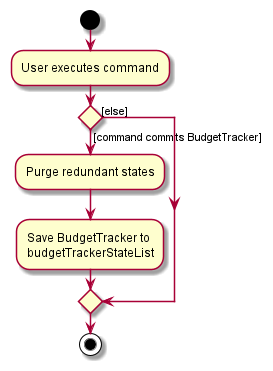
The following activity diagram summarizes what happens when a user executes a new command:
5 Appendix: Requirements
5.1 Product scope
Target user profile: University student who needs to manage their finances.
Value proposition:
Most university students have a limited budget every month and are moving towards financial independence.
During this transition, university students may seek external tools to manage their finances.
Hence, we believe a budget tracker application that records monthly expenses would benefit university
students as they adjust themselves, easing into adulthood.
- Optimised for university students by
- setting monthly psending goals as university students have limited budgets
- allowing university students to categorize their spendings with custom categories suiting their diverse lifestyles
- providing statistics to help university students better visualize their spending habits and make future plans (i.e. to cut down on costs incurred on food next month)
- sending reminders to keep university students on track (i.e. how much money is left in their budget) as they are often busy with school
5.2 User stories
| As a … | I want to … | So that I can… |
|---|---|---|
| university student who wants to manage my finances | add an FR | track my spending history easily |
| university student who wants to manage my finances | delete an FR | recover from mistakes from adding wrong entries of my spending history |
| university student who wants to manage my finances | view all FRs | quickly glance at all my past spendings |
| university student who wants to manage my finances | view all FRs in a particular month | quickly glance at my spending history of a specific month |
| university student who wants to manage my finances | find FRs based on description, amount and/or category | quickly glance at my spending history of the specified fields |
| university student who wants to manage my finances | reset filters on FRs | quickly glance at the original list of financial records |
| university student who has difficulties in managing expenses | set a monthly budget | keep track of my expenses and reduce chances of overspending |
| university student who has difficulties in managing expenses | view my monthly budget | quickly glance at budget set for the given month |
| careless university student who often makes mistakes | undo an incorrectly used command | correct the mistake(s) made |
| careless university student who often makes mistakes | redo an incorrectly used command | correct the mistake(s) made |
| university student who wants to know how much money I can still spend | view my remaining budget for a particular month | be aware of my spending and decide whether I need to be more prudent with my spending |
| university student who wants to visualise my data in a more concise manner | view the past 6 months’ expenditure and budgets | quickly glance and gain insight from my spending patterns |
| university student who wants to visualise my data in a more concise manner | view the total expenses of the current visible list | quickly glance and gain insight from my spending patterns |
| university student who wants to visualise my data in a more concise manner | view the top 5 categories that I spend the most on | quickly glance and gain insight from my spending patterns |
5.3 Use cases
(For all use cases below, the System is the BudgetTracker and the Actor is the user, unless specified otherwise)
Use case: Add a Financial Record
MSS
- Actor requests to add a financial record
- Actor inputs description and amount
- System shows the most recently added financial record
-
Actor acknowledges the addition
Use case ends.
Use case: Delete a Financial Record
MSS
- Actor requests to delete a financial record
- Actor inputs desired index of financial record to be deleted
- System shows the most recently deleted financial record
-
Actor acknowledges the deletion
Use case ends
Extensions
-
2a. The given index is invalid.
-
2a1. System shows an error message.
Use case resumes at step 1.
-
Use case: View a Financial Record
- Actor requests to view a financial record
- Actor inputs desired index of financial record to view
- System shows the financial record with corresponding index
-
Actor completes viewing the desired financial record
Use case ends
Extensions
-
2a. The given index is invalid.
-
2a1. System shows an error message.
Use case resumes at step 1.
-
Use case: View the current month’s Financial Records
- Actor requests to view the current month’s financial records
- System shows the current month’s financial records
-
Actor completes viewing the current month’s financial record
Use case ends
Extensions
-
1a. The current month does not contain any financial records.
-
1a1. System shows an error message.
Use case ends.
-
Use case: Set a budget
- Actor requests to set budget
- Actor inputs desired budget amount
- System shows newly set monthly budget
-
Actor acknowledges newly set monthly budget
Use case ends
Extensions
-
1a. The given budget amount is invalid.
-
1a1. System shows an error message.
Use case resumes at step 1.
-
Use case: View monthly budget
- Actor requests to view monthly budget
- System shows monthly budget
-
Actor completes viewing monthly budget
Use case ends
Extensions
-
1a. Monthly budget is not set.
-
1a1. System shows an error message.
Use case ends.
-
Use case: View remaining budget for the current month
- Actor requests to view remaining budget for the current month
- System shows the remaining budget for the current month
-
Actor completes viewing the remaining budget for the current month
Use case ends
Extensions
-
1a. Monthly budget is not set.
-
1a1. System shows an error message.
Use case ends.
-
Use case: Find financial records of the current month by description, amount and/or category
- Actor requests to find by
Foodcategory - System shows all financial records with
Foodtagged as category -
Actor completes viewing the filtered list for the current month
Use case ends
Extensions
-
1a. No financial records with
Foodcategory found-
1a1. System shows an error message.
Use case ends.
-
-
2a. Actor wishes to further filter the list to view all records with description matching
Breakfast- 2a1. Actor requests to find by
Breakfastdescription -
2a2. System shows all financial records with
Breakfastas description andFoodas categoryUse case ends.
- 2a1. Actor requests to find by
-
3a. Actor wishes to view original list of financial records without filter
- 3a1. Actor requests to reset filter
- 3a2. System shows original list of financial records for the current month
-
3a3. Actor completes viewing the list of financial records
Use case ends.
5.4 Non-Functional Requirements
- Should work on any mainstream OS as long as it has Java
11or above installed. - Should work without internet connection.
- Should be cross-platform.
- Should be able to hold up to 1000 financial records without a noticeable sluggishness in performance for typical usage.
- A user with above average typing speed for regular English text (i.e. not code, not system admin commands) should be able to accomplish most of the tasks faster using commands than using the mouse.
5.5 Glossary
- Mainstream OS: Windows, Linux, Unix, OS-X
- Cross-platform: Able to transfer the software and its data from one OS to another without creating any problem
6 Appendix: Instructions for manual testing
Given below are instructions to test the app manually.
Launch and shutdown
-
Initial launch
-
Download the jar file and copy into an empty folder
-
Double-click the jar file Expected: Shows the GUI with a set of sample contacts. The window size may not be optimum.
-
-
Saving window preferences
-
Resize the window to an optimum size. Move the window to a different location. Close the window.
-
Re-launch the app by double-clicking the jar file.
Expected: The most recent window size and location is retained.
-
Saving data
- Dealing with missing/corrupted data files